food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome in adults
The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines. Like other food allergies FPIES reactions are triggered by eating a particular food.
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Dr Costa Private Children S Allergy Clinic
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults.
. The clinical differences with pediatric FPIES warrant a 91 revision of diagnostic criteria in adults. 1 FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition that occurs in infants and young children although it can rarely affect older children or adults as well.
FPIES presents in two different forms. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. Bryan N Fernandes Robert J Boyle Claudia Gore Angela Simpson Adnan Custovic.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults. While the pathophysiology of FPIES is poorly understood the clinical presentation of acute FPEIS reactions has been well characterized. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES.
Reactions are delayed and begin as soon as 2 hours after ingesting a trigger food. Misguided management of this rare and poorly understood condition. Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration.
The most common triggers include cow milk soy and grains rice barley oats. Food proteininduced enterocolitis-like syndrome in a population of adolescents and adults caused by seafood. Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in infants. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy that manifests with repetitive projectile vomiting within 14 hours following food ingestion frequently accompanied by pallor lethargy and may be followed by diarrhea within 68 hours. Unlike most food allergies symptoms of FPIES do not begin immediately after eating.
These symptoms can lead to severe lethargy change in body temperature and blood pressure. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a nonIgE-mediated food allergic disorder that can manifest with symptoms of projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypotension hypothermia and metabolic derangements. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea.
Vomiting is often followed by a paleness to the skin. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a potentially severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy non-IgE-GI-FA with heterogeneous clinical manifestations. Many allergists report that symptoms suggestive of FPIES are on occasion reported by adult patients and mainly refer to ingestion of seafood.
In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES.
Instead it can take hours before severe symptoms begin. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system. The bad thing about FPIES is that realistically any food can be a trigger.
92 93 94 J urn al P e-p roo f 4 Highlights box 95 96 What is already known about this topic. As a result of these. It typically causes vomiting and bloody diarrhea after consumption of certain foods the trigger foods arent the same for everyone.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults. Unlike typical food allergies symptoms may not be. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome. 97 Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is increasingly recognized 98 in adults with a predominance in women. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion.
FPIES is a cell-mediated delayed hypersensitivity immune reaction in the gastrointestinal system. FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE and cell-mediated food allergic disorder that is characterized by protracted and repetitive vomiting as well as frequent diarrhea. Epub 2012 Jul 24.
Acute FPIES is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food. J Allergy Clin Immunol. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food protein.
Most of the reactions were due to seafood mollusks crustaceans and fish and egg but other foods like peanut almond mushroom corn chicken and duck were also implicated. The most common trigger is shellfish followed by fish egg peanuts almonds chicken and dairy. FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock.
This is different from the common triggers in kids which are dairy soy oats rice and banana among others. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy that affects the gastrointestinal GI tract. The first International Consensus.
1 In about 1520 of the reactions severe dehydration with hypotension and metabolic derangements. Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. An acute form and a chronic form.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
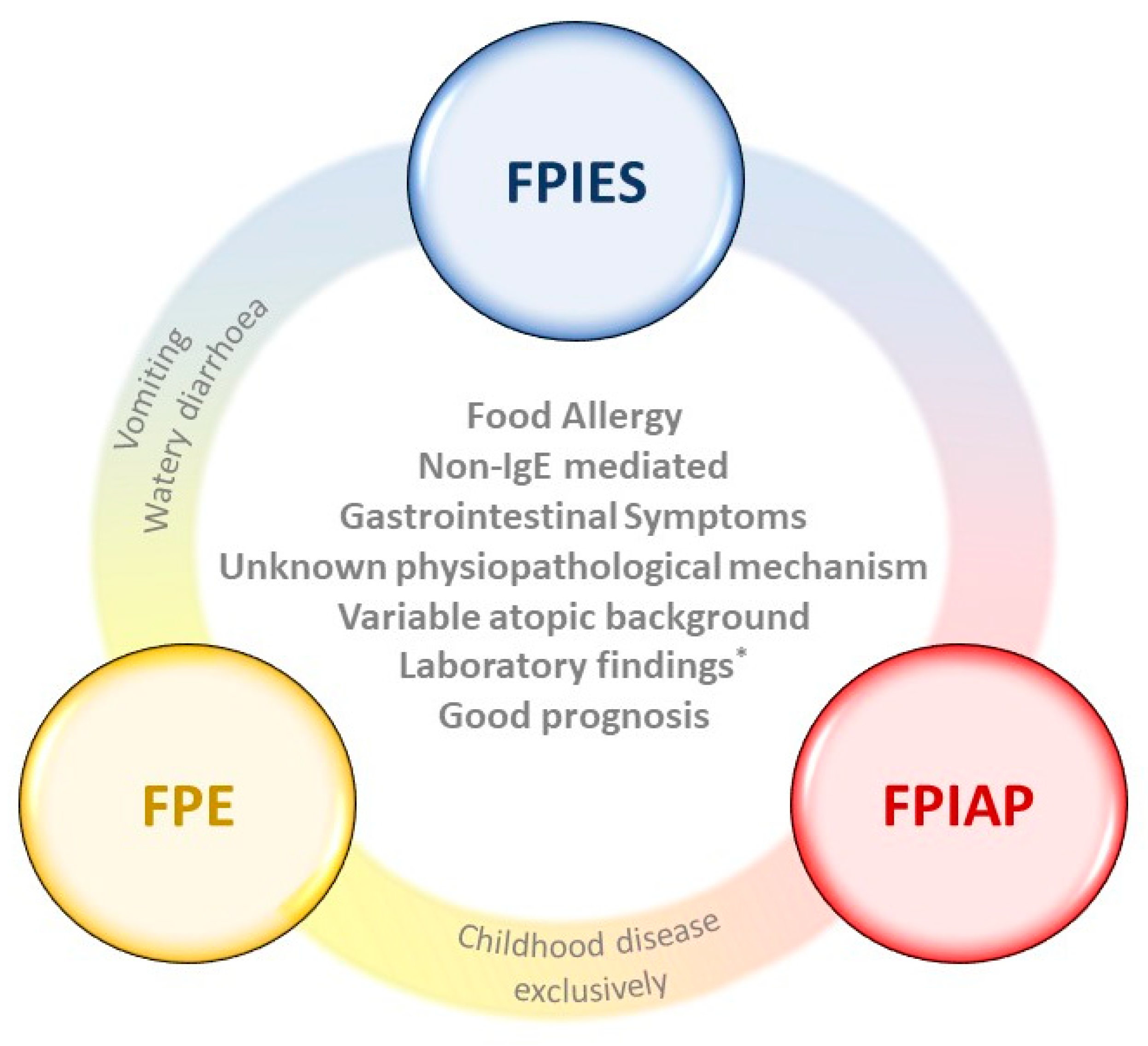
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
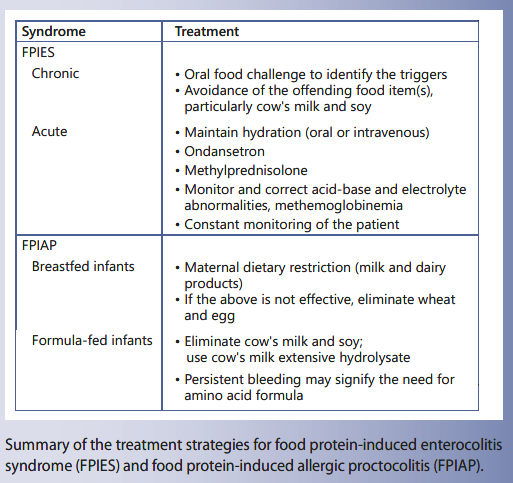
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

International Fpies Association

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

International Consensus Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Executive Summary Workgroup Report Of The Adverse Reactions To Foods Committee American Academy Of Allergy Asthma Immunology Journal

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome As A Cause For Infant Hypotension The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine
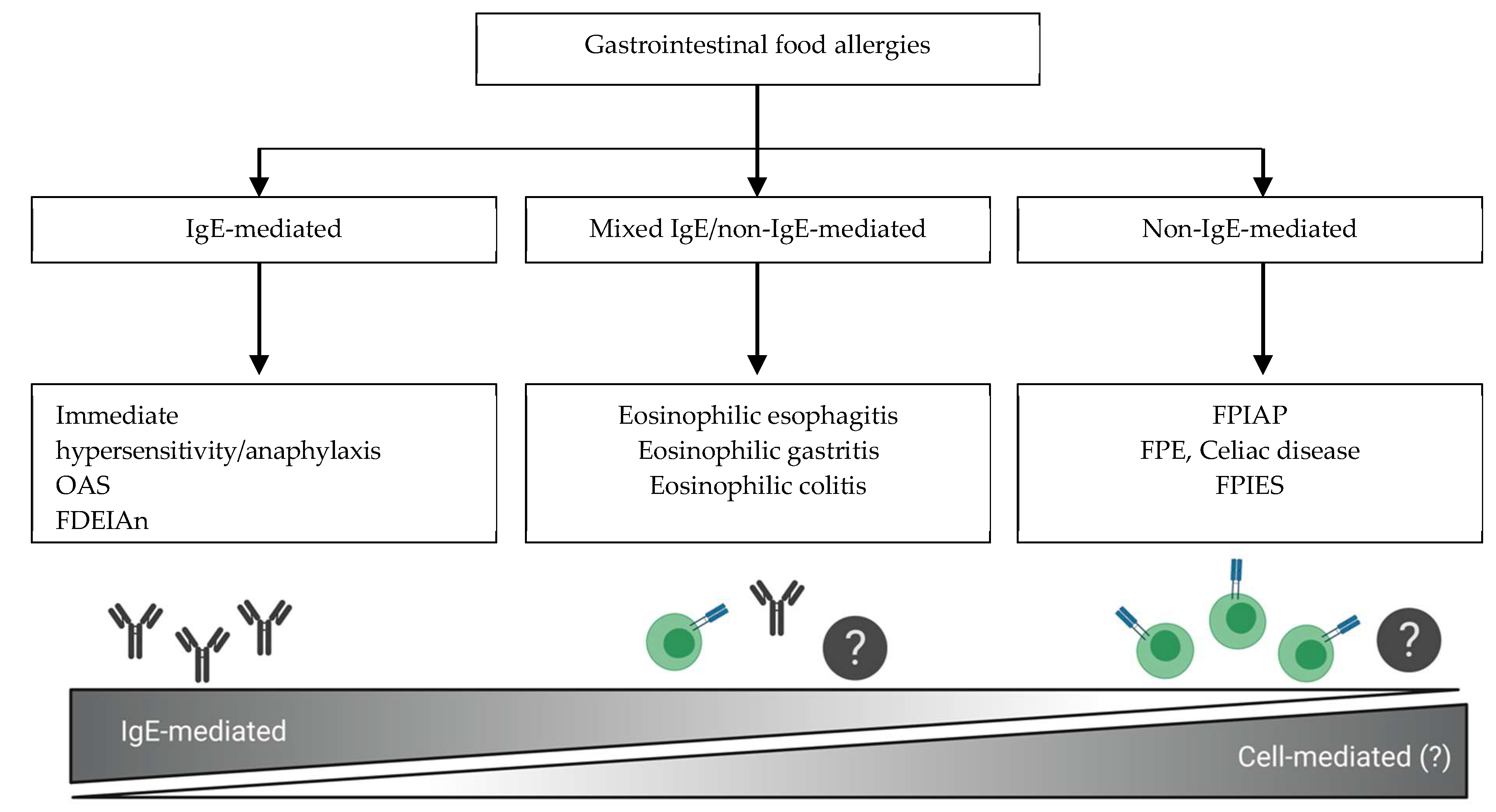
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html
